|
对于最新的稳定版本,请使用 Spring Framework 6.2.10! |
容器概述
这org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext接口表示 Spring IoC
容器,并负责实例化、配置和组装
豆。容器获取有关哪些对象的指令
通过读取配置元数据来实例化、配置和组装。这
配置元数据以 XML、Java 注释或 Java 代码表示。它让
您可以表达构成应用程序的对象和丰富的相互依赖关系
在这些对象之间。
的几个实现ApplicationContext提供接口
与Spring。在独立应用程序中,通常会创建一个
实例ClassPathXmlApplicationContext或FileSystemXmlApplicationContext.
虽然 XML 一直是定义配置元数据的传统格式,但您可以
通过以下方式指示容器使用 Java 注释或代码作为元数据格式
提供少量的 XML 配置以声明方式启用对这些
其他元数据格式。
在大多数应用程序场景中,不需要显式用户代码来实例化一个或
更多 Spring IoC 容器的实例。例如,在 Web 应用程序场景中,一个
简单的八行(或大约)行样板 Web 描述符 XMLweb.xml文件
通常就足够了(请参阅 Web 应用程序的便捷 ApplicationContext 实例化)。
如果您使用 Spring Tools for Eclipse(由 Eclipse 提供支持
开发环境),您可以使用
很少的鼠标点击或击键。
下图显示了 Spring 工作原理的高级视图。您的应用程序类
与配置元数据相结合,以便在ApplicationContext是
创建并初始化,则您拥有完全配置和可执行的系统,或者
应用。
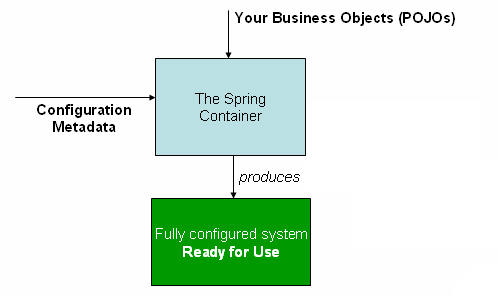
配置元数据
如上图所示,Spring IoC 容器使用 配置元数据。此配置元数据表示您作为 应用程序开发人员,告诉 Spring 容器实例化、配置和汇编 应用程序中的对象。
配置元数据传统上以简单直观的 XML 格式提供, 这是本章的大部分内容,用于传达 Spring IoC 容器。
| 基于 XML 的元数据并不是唯一允许的配置元数据形式。 Spring IoC 容器本身与 配置元数据实际上是写入的。如今,许多开发人员为他们的 Spring 应用程序选择基于 Java 的配置。 |
有关将其他形式的元数据与 Spring 容器一起使用的信息,请参阅:
-
基于注释的配置:使用 基于注释的配置元数据。
-
基于 Java 的配置:定义应用程序外部的 Bean 使用 Java 而不是 XML 文件的类。要使用这些功能,请参阅
@Configuration,@Bean,@Import, 和@DependsOn附注。
Spring 配置至少由一个 Bean 组成,通常不止一个 Bean
容器必须管理的定义。基于 XML 的配置元数据配置了这些
beans 作为<bean/>顶级元素<beans/>元素。Java
配置通常使用@Bean-annotated 方法中的@Configuration类。
这些 Bean 定义对应于构成应用程序的实际对象。
通常,您可以定义服务层对象,持久性层对象,例如
存储库或数据访问对象 (DAO)、表示对象,例如 Web 控制器、
基础结构对象,例如 JPAEntityManagerFactory、JMS 队列等。
通常,不会在容器中配置细粒度域对象,因为
创建和加载通常是存储库和业务逻辑的责任
domain 对象。
以下示例显示了基于 XML 的配置元数据的基本结构:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="..." class="..."> (1) (2)
<!-- collaborators and configuration for this bean go here -->
</bean>
<bean id="..." class="...">
<!-- collaborators and configuration for this bean go here -->
</bean>
<!-- more bean definitions go here -->
</beans>| 1 | 这id属性是标识单个 Bean 定义的字符串。 |
| 2 | 这class属性定义 bean 的类型并使用完全限定的
类名。 |
的值id属性可用于引用协作对象。The XML
用于引用协作对象,在此示例中未显示。有关详细信息,请参阅依赖项。
实例化容器
一个或多个位置路径
供应给ApplicationContext构造函数是资源字符串,允许
容器加载来自各种外部资源的配置元数据,例如
作为本地文件系统,JavaCLASSPATH,依此类推。
-
Java
-
Kotlin
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("services.xml", "daos.xml");val context = ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("services.xml", "daos.xml")|
了解了 Spring 的 IoC 容器后,您可能想了解更多有关 Spring 的 |
以下示例显示了服务层对象(services.xml)配置文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- services -->
<bean id="petStore" class="org.springframework.samples.jpetstore.services.PetStoreServiceImpl">
<property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"/>
<property name="itemDao" ref="itemDao"/>
<!-- additional collaborators and configuration for this bean go here -->
</bean>
<!-- more bean definitions for services go here -->
</beans>以下示例显示了数据访问对象daos.xml文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="accountDao"
class="org.springframework.samples.jpetstore.dao.jpa.JpaAccountDao">
<!-- additional collaborators and configuration for this bean go here -->
</bean>
<bean id="itemDao" class="org.springframework.samples.jpetstore.dao.jpa.JpaItemDao">
<!-- additional collaborators and configuration for this bean go here -->
</bean>
<!-- more bean definitions for data access objects go here -->
</beans>在前面的示例中,服务层由PetStoreServiceImpl类
以及两个类型的数据访问对象JpaAccountDao和JpaItemDao(基于
在 JPA 对象关系映射标准上)。这property name元素引用
javaBean 属性的名称,以及ref元素引用另一个 bean 的名称
定义。这种联系id和ref元素表示
协作对象。有关配置对象依赖项的详细信息,请参阅依赖项。
编写基于 XML 的配置元数据
让 Bean 定义跨越多个 XML 文件会很有用。通常,每个人 XML 配置文件表示架构中的逻辑层或模块。
您可以使用应用程序上下文构造函数从所有这些构造函数加载 Bean 定义
XML 片段。此构造函数采用多个Resource位置,如上一节所示。或者
使用一个或多个出现的<import/>元素从中加载 Bean 定义
另一个或多个文件。以下示例显示了如何执行此作:
<beans>
<import resource="services.xml"/>
<import resource="resources/messageSource.xml"/>
<import resource="/resources/themeSource.xml"/>
<bean id="bean1" class="..."/>
<bean id="bean2" class="..."/>
</beans>在前面的示例中,外部 Bean 定义是从三个文件加载的:services.xml,messageSource.xml和themeSource.xml.所有位置路径都是
相对于执行导入的定义文件,因此services.xml必须位于
与导入的文件相同的目录或类路径位置,而messageSource.xml和themeSource.xml必须位于resources位置低于
导入文件的位置。如您所见,前导斜杠被忽略。但是,鉴于
这些路径是相对的,最好不要使用斜杠。这
要导入的文件的内容,包括顶层<beans/>元素,必须
是有效的 XML bean 定义,根据 Spring Schema。
|
可以使用
相对“../“ 路径。这样做会创建对当前文件之外的文件的依赖关系
应用。特别是,不建议将此引用用于 您始终可以使用完全限定的资源位置而不是相对路径:对于
例 |
命名空间本身提供了导入指令功能。进一步
除了普通 bean 定义之外的配置功能,还可以在选择中使用
Spring 提供的 XML 命名空间——例如,context和util命名空间。
Groovy Bean 定义 DSL
作为外部化配置元数据的进一步示例,bean 定义还可以 在 Spring 的 Groovy Bean Definition DSL 中表示,如 Grails 框架中所知。 通常,此类配置位于“.groovy”文件中,其结构如 以下示例:
beans {
dataSource(BasicDataSource) {
driverClassName = "org.hsqldb.jdbcDriver"
url = "jdbc:hsqldb:mem:grailsDB"
username = "sa"
password = ""
settings = [mynew:"setting"]
}
sessionFactory(SessionFactory) {
dataSource = dataSource
}
myService(MyService) {
nestedBean = { AnotherBean bean ->
dataSource = dataSource
}
}
}这种配置风格在很大程度上等同于 XML bean 定义,甚至
支持 Spring 的 XML 配置命名空间。它还允许导入 XML
bean 定义文件通过importBeans命令。
使用容器
这ApplicationContext是先进工厂能够维护的接口
不同 bean 及其依赖项的注册表。通过使用T getBean(String name, Class<T> requiredType),您可以检索 Bean 的实例。
这ApplicationContext允许您读取 Bean 定义并访问它们,如下所示
示例显示:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
// create and configure beans
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("services.xml", "daos.xml");
// retrieve configured instance
PetStoreService service = context.getBean("petStore", PetStoreService.class);
// use configured instance
List<String> userList = service.getUsernameList(); import org.springframework.beans.factory.getBean
// create and configure beans
val context = ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("services.xml", "daos.xml")
// retrieve configured instance
val service = context.getBean<PetStoreService>("petStore")
// use configured instance
var userList = service.getUsernameList()使用 Groovy 配置,引导看起来非常相似。它有不同的背景 实现类,该类是 Groovy 感知的(但也理解 XML bean 定义)。 以下示例显示了 Groovy 配置:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
ApplicationContext context = new GenericGroovyApplicationContext("services.groovy", "daos.groovy");val context = GenericGroovyApplicationContext("services.groovy", "daos.groovy")最灵活的变体是GenericApplicationContext与阅读器结合使用
委托 — 例如,使用XmlBeanDefinitionReader对于 XML 文件,如下所示
示例显示:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
GenericApplicationContext context = new GenericApplicationContext();
new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(context).loadBeanDefinitions("services.xml", "daos.xml");
context.refresh();val context = GenericApplicationContext()
XmlBeanDefinitionReader(context).loadBeanDefinitions("services.xml", "daos.xml")
context.refresh()您还可以使用GroovyBeanDefinitionReader对于 Groovy 文件,如下所示
示例显示:
-
Java
-
Kotlin
GenericApplicationContext context = new GenericApplicationContext();
new GroovyBeanDefinitionReader(context).loadBeanDefinitions("services.groovy", "daos.groovy");
context.refresh();val context = GenericApplicationContext()
GroovyBeanDefinitionReader(context).loadBeanDefinitions("services.groovy", "daos.groovy")
context.refresh()您可以在同一个ApplicationContext, 从不同的配置源读取 Bean 定义。
然后,您可以使用getBean检索 bean 的实例。 这ApplicationContextinterface 有一些其他方法用于检索 bean,但是,理想情况下,您的应用程序代码永远不应该使用它们。事实上,您的应用程序代码不应该调用getBean()方法,因此根本不依赖于 Spring API。 例如 Spring 与 Web 框架的集成为各种 Web 提供了依赖注入框架组件,例如控制器和 JSF 管理的 bean,让您声明通过元数据(例如自动连接注释)对特定 bean 的依赖关系。